728x90
1. async : function 앞에 붙어 항상 Promise를 반환한다.
- async는 Promise문 코드를 줄여주고 가독성을 높혀준다.
- resolve, reject를 따로 작성할 필요 없다.
1) 에러면 reject로 판단 -> 알아서 catch로 연계 (async + await 문에서는 try + catch를 쓰는데 뒤에 나옴)
2) 성공이면 resolve로 판단 -> 알아서 then으로 연계
*아래 Promise 문을 async로 정리하면
// Promise 를 async 로 정리해보자
const test = function () {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
resolve("성공")
})
}
const test1 = function (something) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
resolve(`${something}했다`)
})
}
const test2 = function (something2) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
resolve(`${something2}구요`)
})
}
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// async 로 줄어보면
const test = async function () {return "성공"}
const test1 = async function (something) {return `${something}했다`}
const test2 = async function (something2) {return `${something2}구요`}
// 화살표 함수로 변환
const test = async () => {return "성공"}
const test1 = async (something) => {return `${something}했다`}
const test2 = async (something2)=> {return `${something2}구요`}
-----------에러일 경우----------------------
const test = async () => {return "성공"}
const test1 = async (something) => {return `${something}했다`}
const test2 = async ()=> {throw new Error("errrr....")}
test()
.then(test1)
.then(test2)
.catch(err => {console.log(err)})
// Error: errrr....
2. await : Promise 함수가 완료될 때까지 기다려라
- await 키워드 오른쪽에는 Promise가 오고 Promise가 완료될 때까지 기다림.
- async 함수 내부에서만 사용가능
- async 문에서 setTimeout 함수를 직접 사용하려면 Promise로 또 감싸줘야 한다. (셋타임아웃은 프라미스를 반환하지 않기 때문에)
📌 예제1
// await
function getName(name){
return new Promise((resolve, reject)=>{
setTimeout(() => {
resolve(name)
}, 2000);
});
};
async function showName(){
const result = await getName("cole") // getName 함수가 끝날때가지 기다렸다가 result에 담아라
console.log(result)
}
showName();
📌 예제2 (then을 활용한 실행문과 await 활용한 실행문)
- then을 활용한 실행문보다 '가독성'이 좋음
// async await setTimeout
function test(){
console.log('성공')
return new Promise((resolve, reject)=>{
setTimeout(()=>{resolve('성공')},2000)
})
}
function test1(something){
console.log('했다')
return new Promise((resolve, reject)=>{
setTimeout(()=>{resolve(`${something}했다`)},2000)
})
}
function test2(something){
console.log('구요')
return new Promise((resolve, reject)=>{
setTimeout(()=>{
resolve(`${something}구요`,2000)
})
})
}
// then 활용한 실행-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
test()
.then(test1)
.then(test2)
.then(console.log);
// await 활용한 실행-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
const speak = async function(){
const result1 = await test()
const result2 = await test1(result1)
const result3 = await test2(result2)
console.log(result3)
}
speak();
성공
했다
구요
성공했다구요
📌 체이닝 비교
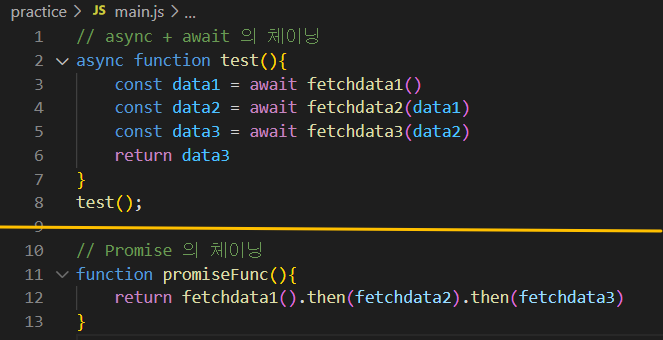
3. try + catch : async & await 문에서 then + catch 역할을 함.
- try{ 실행할 것들 }catch{ 에러나면 실행할 것 }
1) try : 이것들을 시도하다가
2) catch : 에러가 발생하면 이거 실행
// 에러 넣음
function test(){
console.log('성공')
return new Promise((resolve, reject)=>{
setTimeout(()=>{resolve('성공')},2000)
})
}
function test1(something){
console.log('했다')
return new Promise((resolve, reject)=>{
//setTimeout(()=>resolve(`${something}했다`),2000)
setTimeout(() => reject(new Error("errrrr")))}
)}
function test2(something){
console.log('구요')
return new Promise((resolve, reject)=>{
setTimeout(()=>{
resolve(`${something}구요`,2000)
})
})
}
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// try + catch : async + await 문에서 then, catch 역할을 함
const speak = async function () {
try {
const result1 = await test()
const result2 = await test1(result1) // 여기서 콘솔"했다"까지 찍고 에러 걸어둠
const result3 = await test2(result2)
console.log(result3)
} catch (err) {
console.log(err)
}
}
speak();
성공
했다
Error: errrrr
📌 예제3 (Promise.all 로 구현)
- async + await 에서도 Promise.all 을 활용하면 '병렬'로 실행할 수 있다.
// Promise.all 활용
const speak = async function () {
try {
const result1 = await test()
const result2 = await test1(result1)
const result3 = await Promise.all([result1, result2, test2(result2)])
console.log(result3)
} catch (err) {
console.log(err)
}
}
speak();
------------------------------------------------
성공
했다 // 2초뒤
구요 // 2초뒤
[ '성공', '성공했다', '성공했다구요' ] // 한번에
728x90
'html,css,js' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [자바스크립트 중급] Generator 제너레이터 function* (1) | 2023.05.16 |
|---|---|
| [자바스크립트 기초] if 조건문, or and not 논리 연산자 (0) | 2023.05.16 |
| [자바스크립트 중급] Promise // then, catch, finally, Promise.all, Promise.race (0) | 2023.05.15 |
| [자바스크립트 중급] class 클래스, extends, super, overriding (0) | 2023.05.11 |
| [자바스크립트 중급] 상속, 프로토타입 prototype (0) | 2023.05.10 |